Research shows that 60% of homes with basements have moisture problems. Many homeowners struggle to dehumidify their basements, and they’re not alone. Basements tend to be humid spaces naturally. High humidity levels can damage your home’s structure, create mold, and leave unpleasant odors.
Your home’s structure and your family’s health depend on proper basement humidity levels. The ideal basement humidity level ranges between 30% and 50%. Some experts consider up to 60% acceptable. This piece offers practical and proven methods that work to dehumidify your basement. We explain why basements get humid and provide quick fixes along with long-term solutions. You’ll learn everything needed to create a drier and healthier basement environment.
Why Basements Get Humid
Getting to know why your basement gets humid helps you solve the problem. Your basement faces unique moisture challenges compared to other parts of your home.
Cool air and warm air interaction
The science behind basement humidity is simple. Your basement stays cooler than the rest of your house because soil surrounds it. Soil doesn’t conduct heat well. The air temperature drops when warm, humid air from outside or upstairs enters your cool basement. For every 1°F the temperature decreases, relative humidity goes up by 2.2%.
Here’s what happens: Picture an 80°F summer day with 80% relative humidity. This air enters your 68°F basement. The humidity level jumps by about 26.4% (12°F temperature drop × 2.2%). This pushes the relative humidity above 100%. Air can only hold so much moisture. The extra humidity turns into water on cool surfaces like walls, pipes, and floors. This creates that familiar basement dampness.
The problem gets worse during summer months when outdoor humidity climbs. A mild 80°F day with 65% outdoor humidity can make your basement air reach 98% relative humidity. Humidity level above 70% creates perfect conditions where mold thrives.
Moisture from surrounding soil
Your basement sits below ground level, which makes it easy for moisture to seep in. Water finds its way through:
- Capillary suction: Damp soil touching concrete foundations pulls water through tiny concrete pores. This creates rings of dampness at the base of walls. Clay soils make this effect worse.
- Vapor diffusion: Water vapor moves up through porous foundation walls from wet soil into your basement.
- Structural cracks: Water sneaks in through settlement cracks and poorly joined floor joists. Even small cracks let in lots of moisture over time.
The soil around your foundation holds lots of water. This gets worse after heavy rain or melting snow. The water can seep through concrete pores and make indoor air more humid.
Lack of ventilation

Most basements have poor air flow. They have few windows and doors that rarely open. Fresh air has limited chances to get in. This inadequate ventilation creates problems:
- Stagnant air holds onto moisture instead of letting it escape
- Humid air gets trapped with nowhere to go
- Most homes have a “stack effect” where warm air rises. This creates negative pressure in the basement that pulls in moist air through cracks and sump pits
On top of that, moisture problems in about 60% of California basements come from poor ventilation.
Appliances adding moisture
Daily activities and appliances add lots of moisture to your basement:
- Poorly vented washers and dryers release steam
- Fridges and freezers create condensation
- Leaky pipes and ductwork let water in
- Showers and cooking add lots of moisture, especially in finished basements
This extra moisture does more than make you uncomfortable. It damages appliances when warm air hits cold surfaces and forms condensation. This leads to rust and makes appliances less efficient.
These four main causes of basement humidity help you target the right solutions to create a drier, healthier space.
How to Know If Your Basement Is Too Humid
You can save thousands in repair costs by catching basement humidity problems early. A basement might look dry but could hide moisture issues. Let me show you the signs that your basement’s humidity needs your attention.

Condensation on windows or pipes
The first red flag of high humidity is moisture on cool surfaces. Water droplets form when warm, moist air hits cold surfaces like basement windows, metal pipes, or concrete walls. You’ll typically see this condensation:
- On cold water pipes in the basement
- Around basement windows, especially during summer
- On cool basement walls as moisture droplets
- On electronics and metal surfaces
Foggy or wet windows are clear signs of excess humidity. This isn’t just annoying—it shows your basement air has too much moisture. Opening basement windows during hot, humid summer weather makes this worse instead of better.
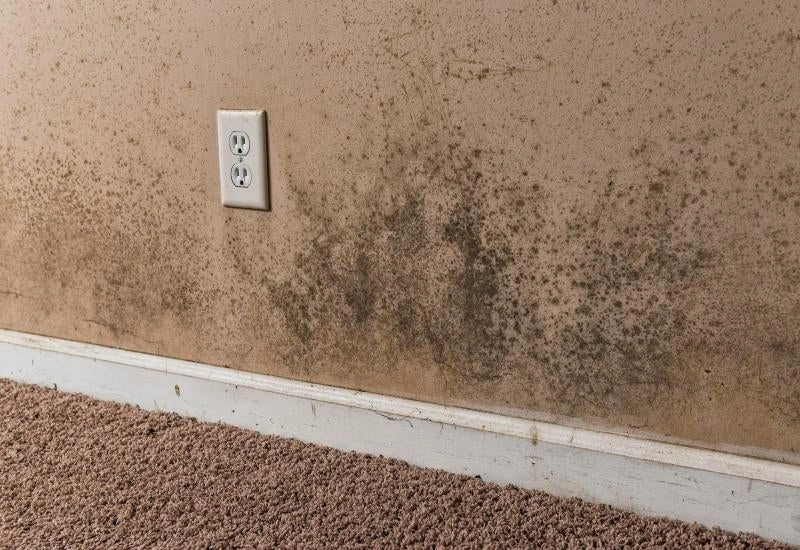
Musty smells and mold
That classic “basement smell” isn’t something you should ignore—it’s a warning sign. A musty or earthy odor usually means mold or mildew is growing. These smells come from:
- Mold spores releasing compounds into the air
- Fungal growth on damp surfaces
- Humid air that can’t escape
The smell gets stronger during spring and fall as windows stay closed and utilities don’t run. These odors can pervade your entire home through ductwork and wall cavities if left unchecked. Advanced cases show visible fungal growth as round, rusty-colored circles.
Rotting wood or damp air
High humidity damages your basement’s environment. The air feels damp, clammy, or sticky once humidity rises above healthy levels. Look for these physical signs:
- Soft, spongy, or discolored wood structures
- Paint peeling or wallpaper bubbling
- White or grayish powder (efflorescence) on unfinished walls
- Damp patches or rings where concrete walls meet the floor
Wood rot is a serious concern. This is a big deal as it means that wood rot destroys about 20 billion board feet of timber yearly in the United States—nowhere near the damage caused by fire. Wood rot problems start once humidity levels exceed 60-70%.
Health symptoms like allergies
Your body acts as a natural humidity detector. Excess basement moisture creates health problems that demonstrate through various symptoms:
- Allergic reactions with sneezing, itchy eyes, and skin irritation
- Coughing, nasal congestion, or throat irritation that won’t go away
- Asthma or other breathing problems getting worse
- Feeling tired or getting headaches after time in the basement
Damp spaces encourage dust mites, bacteria, and mold spores to become airborne, causing these health issues. People who already have breathing problems or weak immune systems face bigger risks in these environments.
Humidity levels that stay above 55-60% consistently put you in the danger zone for all these issues. You’ll need to dehumidify your basement right away to protect your home’s structure and your family’s health.
What Should Basement Humidity Be and How to Measure It
Your basement’s humidity level needs proper monitoring and adjustment to prevent damage. The right balance will protect your home from mold growth and structural issues while keeping the air quality good throughout.
Ideal basement humidity level
Basement humidity works best at 30% to 50% throughout the year [link_1]. This range helps you avoid moisture problems and protect your home’s structure. Humidity below 30% makes your home too dry, which creates gaps around windows and doors. Your wood floors might start to creak too.
High humidity above 50% creates perfect conditions for mold, mildew, and bacteria to thrive. These can harm your health. Too much moisture will damage your walls and carpets, and your home and belongings might start to rot.
Seasonal changes affect ideal humidity levels. Summer humidity should stay under 60%. Winter levels typically range from 20% to 40%, depending on your location. People living in colder areas usually see lower humidity during winter months.
Using a hygrometer
You need a hygrometer to measure your basement’s humidity accurately. These devices track water vapor in the air and give you exact moisture readings. Simple digital hygrometers cost less than $10 and run on button batteries. They are available to most homeowners.
Put your hygrometer in a central basement spot with good air flow. Stay away from windows, doors, or vents that might affect the readings. Most hygrometers come pre-adjusted, but you should verify their accuracy.
You can choose between digital and analog models. Digital versions offer advanced sensors and can log data. Analog ones cost less but need manual adjustment.
When to take action
Your hygrometer readings tell an important story: 30-50% means normal conditions, over 50% shows too much moisture, and under 30% indicates it’s too dry. Readings outside these ranges mean you should intervene.
Act quickly if you see:
- Condensation on windows, pipes, or walls
- Musty, damp smells that won’t go away
- Mold growing on surfaces
- Paint or wallpaper coming off
- White, powdery deposits (efflorescence) on concrete
Check your basement’s moisture levels weekly. Regular monitoring helps catch problems early. Fixing moisture sources works better than dealing with the after-effects.
Simple Fixes to Start Dehumidifying Your Basement
You need to act fast once you spot high humidity in your basement. Here are some proven solutions that work without breaking the bank or requiring major renovations.

Open windows and use fans
Your basement needs fresh air when outdoor humidity drops below indoor levels. Many people get this wrong, but this method works only if the air outside is drier than inside.
Here’s how to move air effectively:
- Set up ceiling or box fans near windows to draw in fresh air
- Put fans in spots that create cross-ventilation
- Box fans in windows work as a quick fix (costing $50-$250)
Air that keeps moving stops moisture from settling on surfaces and blends dry and humid air pockets. The fans help spread heat evenly throughout the space, so condensation drops.
Vent appliances properly
Your household appliances add moisture to the basement by a lot. Make sure clothes dryers, stoves, and kerosene heaters vent outside directly. Even your stove creates water vapor that raises humidity if it’s not vented right.
Take wet items outside to dry after heavy rain or flooding hits your basement. You should then use fans to boost airflow through the space.
Use portable dehumidifiers
A portable dehumidifier ranks among the best quick fixes. You can move these units around to tackle damp spots in your basement. The dehumidifier works best in an open, central spot – just remember to empty its tank often.
The EPA says basement humidity should stay under 60% to stop mold and mildew. A good dehumidifier helps maintain levels between 30% and 50% after you fix the immediate moisture problems.
Keep doors open for airflow
Leave interior doors open as much as possible to let air flow through your basement. This simple change makes a huge difference in how air moves between your basement and the rest of your house.
Your basement benefits from fresh air even without windows. Open interior doors reduce stagnant spots where moisture builds up. This no-cost solution helps dry out your basement naturally all year long, unless you need to close doors for heating or cooling.
Long-Term Basement Dehumidification Solutions
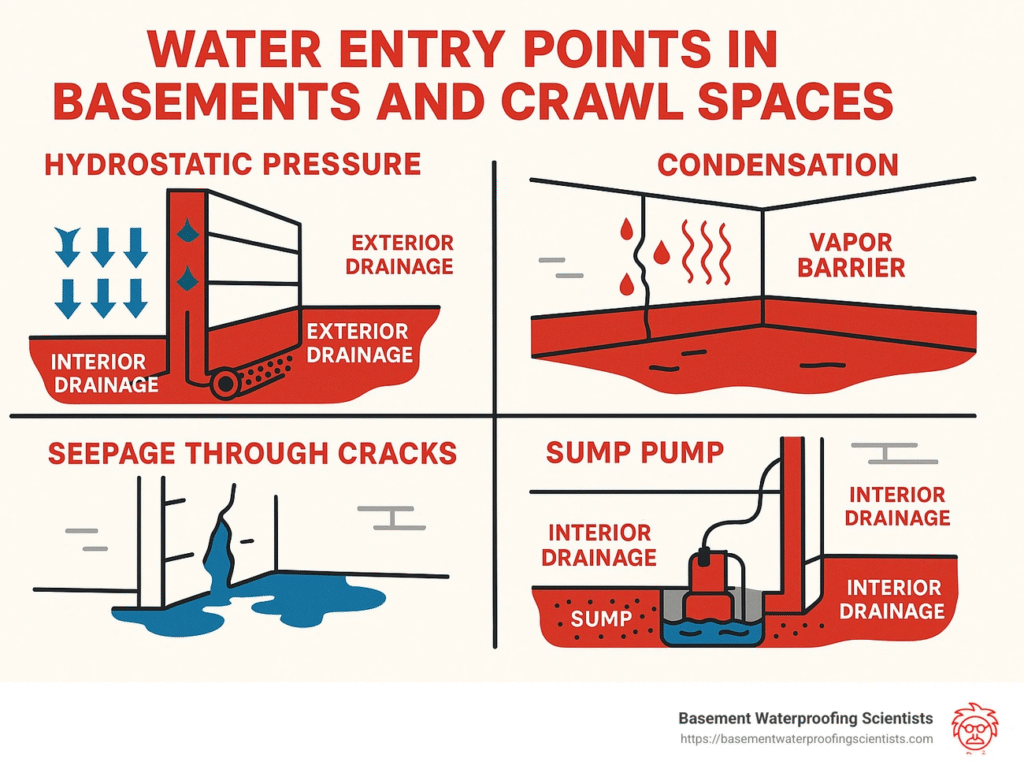
Structural improvements create lasting humidity control in basements. These permanent solutions tackle why moisture problems happen, unlike temporary fixes that don’t last.
Seal cracks and leaks
Your basement needs a thorough inspection of its walls, floors, and foundation to spot visible cracks or gaps. Small cracks let water seep in steadily. Quality polyurethane injection kits seal hairline cracks well. Surface caulking or hydraulic cement packing won’t work long-term and might make things worse.
New cracks need quick attention. Quick fixes now prevent bigger moisture problems later.
Install a sump pump
A sump pump moves groundwater away from your foundation. These systems sit at your basement’s lowest spot and catch rising water before it creates indoor moisture problems.
You can choose from:
- Submersible pumps (quieter, most common)
- Battery backup systems (work during power outages)
- Water-powered pumps (environmentally friendly)
You’ll need professional help with installation since it involves concrete work and proper drainage setup.
Improve insulation and vapor barriers
Vapor barriers stop moisture from moving through basement walls. These materials block water vapor and guide moisture to controlled areas.
Best protection comes from:
- Fluid-applied barriers on concrete walls work better than sheet membranes
- Closed-cell spray foam insulation offers both insulation and vapor barrier benefits
- Continuous vapor barriers without gaps
Your home’s humidity levels drop and mold stays away with these systems.
Maintain gutters and downspouts
Clean gutters affect basement humidity a lot. They stop water from soaking the soil near your foundation.
Working gutters help by:
- Moving rainwater away from your home’s foundation
- Keeping your house’s surroundings dry
- Reducing groundwater pressure on foundation walls
- Limiting indoor humidity by blocking outside moisture
Regular gutter maintenance remains one of the most affordable ways to control humidity.
Conclusion
Your basement needs watchfulness and a complete approach to maintain proper humidity levels. Basements naturally draw in moisture through different mechanisms, and controlling this moisture is crucial for your home’s structure and your family’s health.
A hygrometer helps you track your basement’s moisture levels. Keep the levels between 30-50%. Don’t wait for visible damage – act fast if readings go beyond this range.
Strategic fan placement, proper appliance venting, and portable dehumidifiers provide quick relief while you plan flexible solutions. Keeping interior doors open also helps air flow better throughout your basement space.
Long-term protection requires fixing the mechanisms at work. You need to seal foundation cracks, install reliable drainage systems, and apply proper insulation to keep moisture out of your basement. Your home’s exterior drainage system should direct water away from foundation walls.
Note that dry basements require consistent effort. Managing basement humidity might feel daunting at first, but a systematic approach with quick fixes and permanent improvements will create a healthier, more comfortable space. Your work to maintain ideal humidity levels protects your basement, your home’s value, and your family’s health.
FAQs
Q1. What is the ideal humidity level for a basement? The ideal humidity level for a basement is between 30% and 50%. Maintaining this range helps prevent mold growth, structural damage, and ensures good air quality. In summer, it’s acceptable to keep levels slightly higher, up to 60%, while in winter, levels between 20% and 40% are generally recommended.
Q2. How can I reduce humidity in my basement without a dehumidifier? You can reduce basement humidity without a dehumidifier by improving ventilation (opening windows and using fans), properly venting appliances, sealing cracks and leaks, and using moisture-absorbing materials like silica gel or baking soda. Additionally, keeping interior doors open can help improve air circulation throughout the space.
Q3. What are the signs of excessive humidity in a basement? Signs of excessive humidity in a basement include condensation on windows or pipes, musty odors, visible mold growth, peeling paint or wallpaper, and damp or sticky air. You may also notice rotting wood, white powdery deposits on concrete walls, or experience allergy-like symptoms when spending time in the basement.
Q4. How often should I check my basement’s humidity levels? It’s recommended to check your basement’s humidity levels regularly, ideally on a weekly basis. Use a hygrometer placed in a central location to get accurate readings. Consistent monitoring helps you catch and address moisture problems before they escalate into more serious issues.
Q5. What are some long-term solutions for basement humidity control? Long-term solutions for basement humidity control include sealing foundation cracks, installing a sump pump, improving insulation and vapor barriers, and maintaining proper exterior drainage through well-functioning gutters and downspouts. These measures address the root causes of moisture problems and provide lasting protection against excess humidity.
